Phylum Cnidaria (formerly known as coelenterate) includes about 9000 species. Some are found in fresh water, but the greater number are marine. Coelenterates (Gr. koilos, hollow+enteron, gut) are the simplest of eumetazoans. This interesting group of animals take its name from the large cavity in the body that serves as the intestine. They include the hydra, jellyfish, sea anemones and corals.
.png)
- They are aquatic, mostly marine and a few are fresh water
- Tissue grade of organization: organs and organ system are absent.
- They are diploblastic.
- Body is formed of two layers of cells, viz., an outer ectoderm and an inner endoderm with a non-cellular jelly like layers of mesoglogea in between.
- Radial symmetry with oral and aboral ends, no definite head.
- A central cavity called gastrovascular cavity which opens to exterior by the mouth. Anus is absent.
- Digestion is both intracellular and extracellular.
- Presence of stinging cells or cnidoblast in the ectoderm. The cnidoblast cells possess a capsule called nematocyst containing poisonous fluid. The cnidoblast cells are defensive cells used to kill or paralyses other preys and enemies.
- They are acoelomates. i.e. there is no separation between the digestive cavity and the general body cavity.
- Respiration and excretion occur by diffusion through the body surface.
- Nervous system is primitive and formed of a network of nerve cells and fibres throughout the body.
- Reproduction is by both sexual and asexual means. Fertilized eggs may develop into a larva called planula.
- An alternation of generations or metagenesis is found in the life history i.e. the asexual polyploid generation alternates with the sexual medusoid generation
🎯Examples of Coelenterata (Cnidaria)
- Physalia (Portuguese man-of-war)
.png)
.png)
.png)
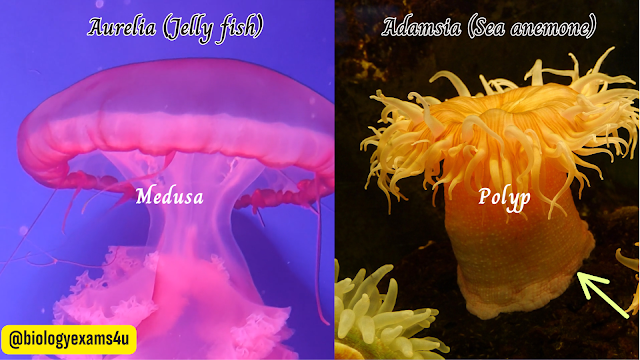
.png) Polyp and Medusa body forms: Cnidarians have two types of body forms, viz., polyp and medusa. (Polyp vs Medusa)
Polyp and Medusa body forms: Cnidarians have two types of body forms, viz., polyp and medusa. (Polyp vs Medusa)- The polyp is cylindrical and usually fixed. It represents the asexual stage.
- The medusa is umbrella like and usually free swimming. It represents the sexual phase.
🎯Phylum Cnidaria is divided into three classes
- A division of labour is seen in the colony because each type of zooid is specialized to perform a specific function.
- Physalia and Halistemma are example of polymorphic colonies
Examples: Sea anemone and corals like Fungia, Favia and Madrepora.
🎯Key Point Phylum Coelenterata (Cnidaria)
Phylum Coelenterata (Cnidaria) They are aquatic, mostly marine, sessile or free-swimming, radially symmetrical animals The name cnidaria is derived from the cnidoblasts or cnidocytes (which contain the stinging capsules or nematocysts) present on the tentacles and the body. Cnidoblasts are used for anchorage, defense and for the capture of prey Cnidarians exhibit tissue level of organisation and are diploblastic. They have a central gastro-vascular cavity with a single opening, mouth on hypostome. Digestion is extracellular and intracellular. Some of the cnidarians, e.g., corals have a skeleton composed of calcium carbonate. Cnidarians exhibit two basic body forms called polyp and medusa. The former is a sessile and cylindrical form like Hydra, Adamsia, etc. whereas, the latter is umbrella-shaped and free-swimming like Aurelia or jelly fish. Those cnidarians which exist in both forms exhibit alternation of generation (Metagenesis), i.e., polyps produce medusae asexually and medusae form the polyps sexually (e.g., Obelia).
🎯Quiz on Phylum Coelenterates | Cnidarians
.jpg)