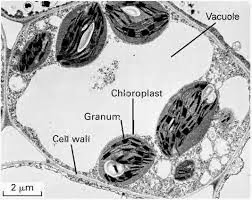
Vacuoles may be defined as a non living reservoir, bounded by a differentially or selectively permeable membrane, the tonoplast. The structure of tonoplast is similar to that of single unit membrane. Depending upon the content and functions, vacuoles are of four type: sap vacuoles, contractile vacuoles, food vacuoles and gas (air) vacuoles.
 Vacuoles and their contents are considered to be distinct from the cytoplasm and are classified as ergastic. Vacuoles play a major role in autophagy, maintaining a balance between biogenesis (production) and degradation of many substances and cell structures. They also aid in destruction of invading bacteria or of misfolded proteins that have begun to buildup within the cell.
Vacuoles and their contents are considered to be distinct from the cytoplasm and are classified as ergastic. Vacuoles play a major role in autophagy, maintaining a balance between biogenesis (production) and degradation of many substances and cell structures. They also aid in destruction of invading bacteria or of misfolded proteins that have begun to buildup within the cell.
Functions of Vacuole
2. Isolating materials that might be harmful or a threat to the cell.
3. Containing waste products.
4. Vacuoles have a role in enlargement of cells during their growth by their own enlargement, endosmosis and providing stored materials.
5. Maintaining internal hydrostatic pressure or turgor within the cell.
6. Maintaining an acidic internal pH.
7. Exporting unwanted substances from the cell.
8. Enabling the cell to change shape.
9. Proteins found in the tonoplast control the flow of water into and out of the vacuole through active transport, pumping potassium ions into and out of the vacuolar interior.
10. Tannins, alkaloids and toxins stored in vacuoles protect the plants from herbivorous animals.

thanks
ReplyDeleteThanks
ReplyDeleteThanks
ReplyDeleteThanks for your help
ReplyDeleteThanks for your help
ReplyDelete