Neurons are the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system. They are responsible for receiving, processing, and transmitting information throughout the body. Neurons are made up of three main parts: the cell body, the dendrites, and the axon.
In
the last post, we discussed the classification of neurons based on structure.
In this post let us understand the classification of neurons based on function.
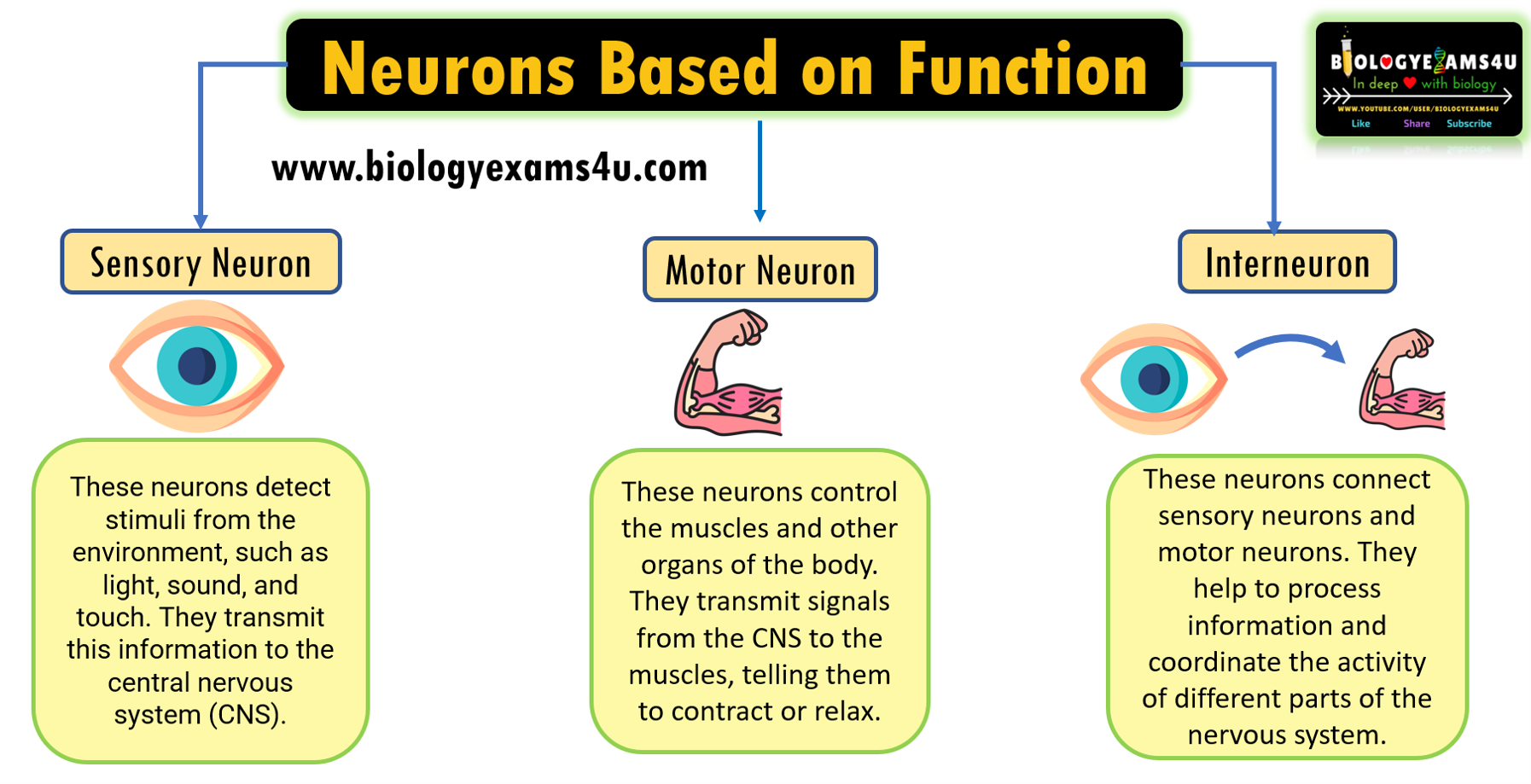
Based
on function, neurons are classified into three, sensory neuron, motor neuron and
interneuron.
1.
Sensory neuron
- These neurons detect stimuli from the environment, such as light, sound, and touch.
- They transmit this information to the central nervous system (CNS).
- They have long dendrites that extend from the cell body to receive signals from sensory receptors. The signals are then transmitted to the CNS along the axon.
- Sensory neurons can be classified into different types based on the type of information they collect. For example, there are visual neurons, auditory neurons, and touch neurons.
2.
Motor neuron
- Motor neuron responsible for controlling the body's movements.
- They have long axons that extend from the cell body to the muscles.
- The signals from CNS is transmitted by the motor neurons to the muscles leading to relaxation or contraction, which results in movement.
- Motor neurons can be classified into two types: upper motor neurons and lower motor neurons.
- Upper motor neurons are in the brain, and they send signals to the lower motor neurons in the spinal cord.
- Lower motor neurons then send signals to the muscles.
3.
Interneuron
- Interneurons are the most common type of neuron in the CNS.
- They connect sensory neurons and motor neurons, and they also connect different areas of the CNS.
- Interneurons create neural circuits, enabling communication between sensory or motor neurons and the central nervous system. They act as a “middle-man” between sensory and motor neurons, and connect to other interneurons, allowing them to communicate with one another. The primary function of interneurons is integration, carrying sensory information and regulating motor activity.
- Interneurons play a major role in many different higher functions, including learning, memory and decision-making.
Tags:
Motor neuron and Interneuron
neurobiology mcat
neuron classification A level
neuron classification AP biology
Neurons Classification function
neurons structure
neuroscience
sensory neuron function